Page 15 - Annual Report 2020
P. 15
New tools in cancer risk identification and prevention. Alkyl DNA adducts are cytotoxic and mutagenic DNA lesions that arise from exposure of cells to numerous environmental carcinogens and cellular metabolites. Some of the most toxic alkyl DNA adducts are induced by commonly used anti-cancer drugs. DNA modifications induced
by alkylating agents play significant roles in both the development and treatment of cancer. To understand how alkyl DNA adducts contribute to mutagenesis, cancer development and treatment, it is imperative to be able to examine complete, genome-wide profiles of these lesions and investigate how factors (such as modifications
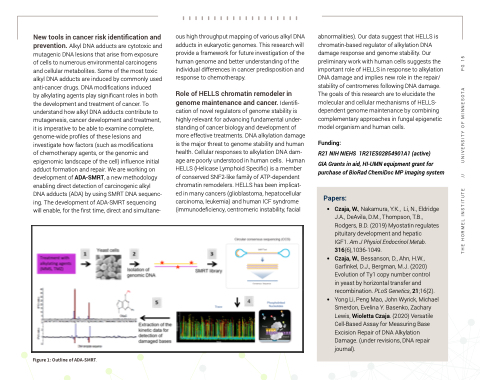
of chemotherapy agents, or the genomic and epigenomic landscape of the cell) influence initial adduct formation and repair. We are working on development of ADA-SMRT, a new methodology enabling direct detection of carcinogenic alkyl DNA adducts (ADA) by using SMRT DNA sequenc- ing. The development of ADA-SMRT sequencing will enable, for the first time, direct and simultane-
ous high throughput mapping of various alkyl DNA adducts in eukaryotic genomes. This research will provide a framework for future investigation of the human genome and better understanding of the individual differences in cancer predisposition and response to chemotherapy.
Role of HELLS chromatin remodeler in genome maintenance and cancer. Identifi- cation of novel regulators of genome stability is highly relevant for advancing fundamental under- standing of cancer biology and development of more effective treatments. DNA alkylation damage is the major threat to genome stability and human health. Cellular responses to alkylation DNA dam- age are poorly understood in human cells. Human HELLS (Helicase Lymphoid Specific) is a member of conserved SNF2-like family of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers. HELLS has been implicat- ed in many cancers (glioblastoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, leukemia) and human ICF syndrome (immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, facial
abnormalities). Our data suggest that HELLS is chromatin-based regulator of alkylation DNA damage response and genome stability. Our preliminary work with human cells suggests the important role of HELLS in response to alkylation DNA damage and implies new role in the repair/ stability of centromeres following DNA damage. The goals of this research are to elucidate the molecular and cellular mechanisms of HELLS- dependent genome maintenance by combining complementary approaches in fungal epigenetic model organism and human cells.
Funding:
R21 NIH NIEHS 1R21ES02854901A1 (active)
GIA Grants in aid, HI-UMN equipment grant for purchase of BioRad ChemiDoc MP imaging system
Figure 1: Outline of ADA-SMRT.
Papers:
• Czaja, W., Nakamura, Y.K., Li, N., Eldridge J.A., DeAvila, D.M., Thompson, T.B., Rodgers, B.D. (2019) Myostatin regulates pituitary development and hepatic
IGF1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
316(6),1036-1049.
• Czaja, W., Bessanson, D., Ahn, H.W.,
Garfinkel, D.J., Bergman, M.J. (2020) Evolution of Ty1 copy number control in yeast by horizontal transfer and recombination. PLoS Genetics, 21;16(2).
• Yong Li, Peng Mao, John Wyrick, Michael Smerdon, Evelina Y. Basenko, Zachary Lewis, Wioletta Czaja. (2020) Versatile Cell-Based Assay for Measuring Base Excision Repair of DNA Alkylation Damage. (under revisions, DNA repair journal).
THE HORMEL INSTITUTE // UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA PG 15